The Evolution of Web Search: How AI and ML Are Reshaping the Industry
- Victor Aynbinder
- Tools & Tips, AI, Technology
- 11 Nov, 2024
The way we search the web has changed dramatically in recent years. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into search technology has transformed what was once a simple keyword lookup process into an intelligent, conversational experience that understands user intent and delivers more relevant results. This shift reflects the growing impact of AI and ML on web search, and it is reshaping the industry at large.
The Rise of Google and the Evolution of Search Engines
In the early days of the internet, web search was a straightforward affair. Search engines like AltaVista, Yahoo, and Lycos competed for dominance, each offering basic keyword matching capabilities. Then, Google entered the scene in the late 1990s, bringing a revolutionary algorithm called PageRank, which used links to determine the relevance of a page. This approach quickly set Google apart, allowing it to provide more accurate search results than its competitors. As Google gained popularity, many other players struggled to keep up. Notable names like AltaVista and Ask Jeeves (not to be confused with the hilarious duo from Jeeves and Wooster) eventually faded into obscurity, while Google emerged as the dominant force in web search.
The competition was fierce, but only a few survived. Bing, Microsoft's offering, managed to carve out a small niche, while others like Yahoo transitioned to using Bing's search technology. The early days of search were a battleground, and Google emerged as the clear winner, setting the stage for what was to come.
How Google Maintains Its Dominance in Search
Google's search engine is powered by a sophisticated combination of algorithms, data analysis, and AI technologies. It ranks pages based on relevance and authority, using signals like backlinks, page content, and user behavior. Google also monetizes its search engine through advertising—specifically, its Google Ads platform, where advertisers bid on keywords to display ads at the top of search results. This pay-per-click model has been incredibly lucrative, making Google one of the wealthiest companies in the world.
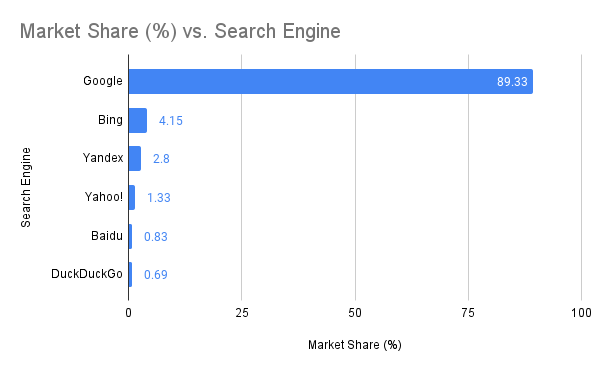
Currently, Google holds an overwhelming share of the search market—almost 90% globally. This dominance is maintained not only through superior technology but also strategic partnerships. For instance, Google paid Apple $20 billion in 2022 to be the default search engine on Safari, ensuring that iPhone users are directed to Google. This partnership is so significant that it constitutes a considerable portion of Apple's services revenue (source).
| Search Engine | Market Share (%) |
|---|---|
| almost 90% | |
| Bing | 4.15 |
| Yandex | 2.8 |
| Yahoo! | 1.33 |
| Baidu | 0.83 |
| DuckDuckGo | 0.69 |
However, Google's dominance has not been without criticism. Many users have complained that Google search has become cluttered with ads, making it harder to find organic results. The rise in ads and perceived decline in relevance have led some to question whether Google's supremacy is waning. The Freakonomics Radio episode titled "Is Google Getting Worse? (Update)" explores this issue in depth, discussing the challenges Google faces as it tries to balance profitability with user satisfaction (Listen to the episode here).
AI and ML in Search: Rising Competition and Innovations
In recent years, competition in the search space has heated up, particularly with the rise of AI-driven search alternatives. OpenAI's new search feature, integrated with ChatGPT, represents a direct challenge to Google's dominance. Released less than two weeks ago, this feature is already making an impact on people's search habits. Soon to be available for free, this feature allows users to interact with search in a conversational manner, bypassing traditional search engines entirely (source).
Google has also used its browser, Google Chrome, as a means of controlling the flow of data and maintaining its grip on the search market. However, OpenAI's ChatGPT has started promoting a Chrome extension that redirects searches to ChatGPT, effectively bypassing Google. This extension is already influencing search habits, potentially shifting user behavior over time. You can check out the extension here: ChatGPT Search Chrome Extension. While the extension essentially redirects users to ChatGPT for search results, it represents a significant threat to Google by potentially changing user preferences.
Competitors Reshaping the Search Landscape
Other competitors have also tried to break into the search market. Neeva, a subscription-based search engine focused on privacy, struggled due to the challenge of convincing users to pay for search services in a market dominated by free options. Cuil, an ambitious project started by former Google engineers, faced issues with poor search result quality and scalability, leading to its failure. Despite their unique approaches, both ultimately failed to gain traction and have since closed down.
Newer competitors are attempting to carve out niches by focusing on different aspects of the search experience. These competitors can be grouped into categories based on their focus:
- Privacy-Focused: Brave emphasizes privacy and ad-blocking to provide a secure browsing experience.
- AI-Driven Search: Perplexity offers a conversational search experience similar to ChatGPT, while Andi focuses on providing a more personalized and visual search experience.
- Developer-Oriented: Tavily is a specialized search engine designed primarily for AI agents and developers, offering customizable search options and efficient integration with LLMs.
- Customizable Search Tools: You.com allows users to customize their search with different apps and tools, creating a more tailored search experience.
These players are pushing the boundaries of what search can be, each with its own advantages over Google, such as enhanced privacy, innovative interfaces, or more relevant, ad-free results.
The Future of Web Search: AI and ML at the Core
The race for dominance in web search is still very much alive. While Google still controls the majority of the market, it faces increasing threats to its core business from both established companies and innovative startups. Companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Perplexity are pushing the boundaries of AI and search, offering alternatives that could reshape how we find information online.
Competing with Google's core business requires substantial financial resources, and companies like OpenAI, Anthropic, and Perplexity are securing significant funding to challenge Google's dominance. For instance, OpenAI recently raised $6.6 billion, elevating its valuation to $157 billion (source). Similarly, Perplexity AI is in the final stages of raising $500 million, which would triple its valuation to $9 billion (source). Additionally, Anthropic is reportedly in early talks to raise new funding that could bring its valuation to $40 billion (source). These substantial investments indicate that these companies are well-positioned to compete in the search market.
The rapid advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) illustrate how quickly the landscape can change. ChatGPT, released by OpenAI on November 30, 2022, quickly gained popularity for generating human-like responses and has seen significant improvements since. While LLMs may not evolve endlessly with each iteration, the companies behind them are constantly innovating, and their impact on web search is only growing. Google's dominance is being challenged in ways that were unthinkable just a few years ago, and the future of search is more uncertain—and more exciting—than ever.
For more insights on how ChatGPT Canvas is starting to take over Google's Document tools, check out this related blog post: How ChatGPT is Changing the Game for Google Docs.
Bonus: A Personal Anecdote
While writing this article, I wanted to mention Neeva but couldn’t remember the name of the startup, the founders, or when it closed down. I remembered hearing about it on a Freakonomics Radio episode, so I decided to search for it. I used Google Gemini, Perplexity, ChatGPT, You, and Brave, and only ChatGPT gave me the right and straight-to-the-point answer. It goes to show that even the giants can be outperformed in certain situations.